Table of Contents
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 was a catastrophic natural disaster that occurred on October 8, 2005, in the Pakistan-administered portion of the Kashmir region known as Azad Kashmir and the North-West Frontier Province of Pakistan. The earthquake had a magnitude of 7.6 and also affected adjacent parts of India and Afghanistan. It resulted in the loss of over 79,000 lives and caused more than 32,000 buildings to collapse in Kashmir.
This earthquake is significant in South Asia’s history as it was one of the deadliest natural disasters to have ever occurred in the region. The event had a profound impact on the people of Kashmir and the surrounding areas, causing widespread destruction and loss of life. The earthquake also highlighted the need for better disaster management and emergency response systems in the region. Let’s delve into this topic.
The Day Earth Shook: October 8, 2005
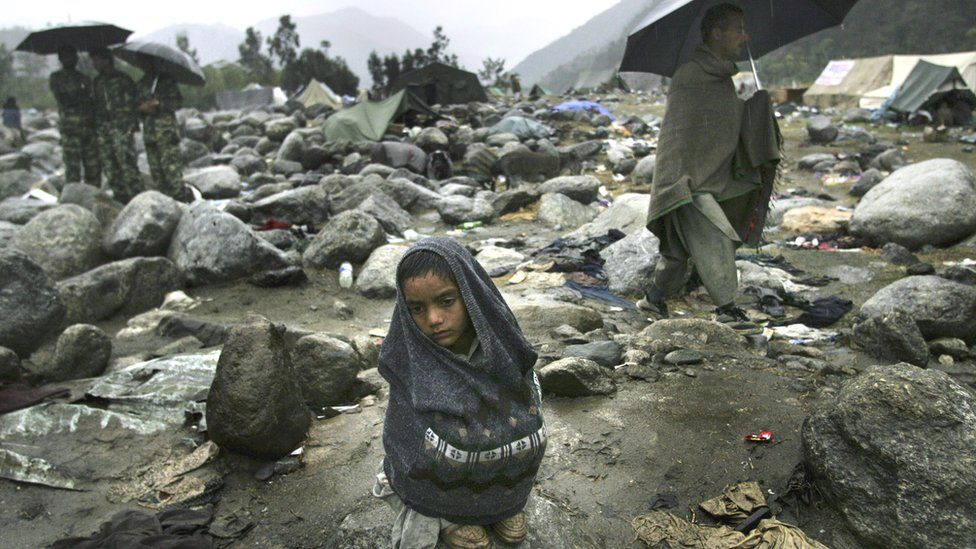

Time and Date of the Earthquake
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 occurred on October 8, 2005, at 8:50:39 AM Pakistan Standard Time.
Epicenter and Affected Regions
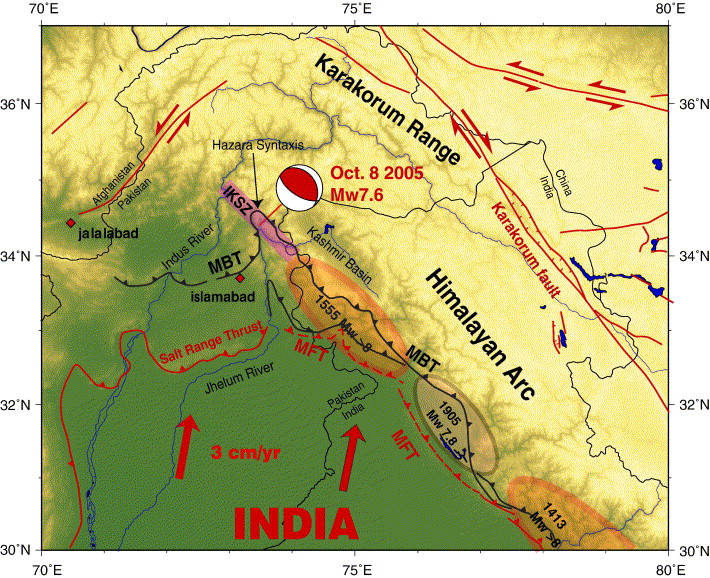
The epicenter of the earthquake was located near the city of Muzaffarabad in Azad Jammu and Kashmir, a territory under Pakistan. The earthquake also affected nearby Balakot in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and some areas of Jammu and Kashmir, India. The earthquake had a magnitude of 7.6 and was felt across South Asia, including parts of Afghanistan and India. The event caused widespread destruction and loss of life, with over 79,000 people losing their lives in Pakistan-administered Kashmir alone. The earthquake also left an estimated 4 million people homeless.
Seismological Analysis
Causes: Collision of Eurasian and Indian Tectonic Plates
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 was caused by the collision of the Eurasian and Indian tectonic plates. The Indian plate is moving northward at a rate of approximately 47 mm per year and is being subducted beneath the Eurasian plate. The collision between these two plates has resulted in the formation of the Himalayan mountain range and has led to frequent seismic activity in the region.
Magnitude and Intensity of the Earthquake
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 had a magnitude of 7.6 on the Richter scale. The earthquake was felt across South Asia, including parts of Afghanistan and India. The intensity of the earthquake was highest in Muzaffarabad, where it was recorded as VIII on the Mercalli intensity scale.
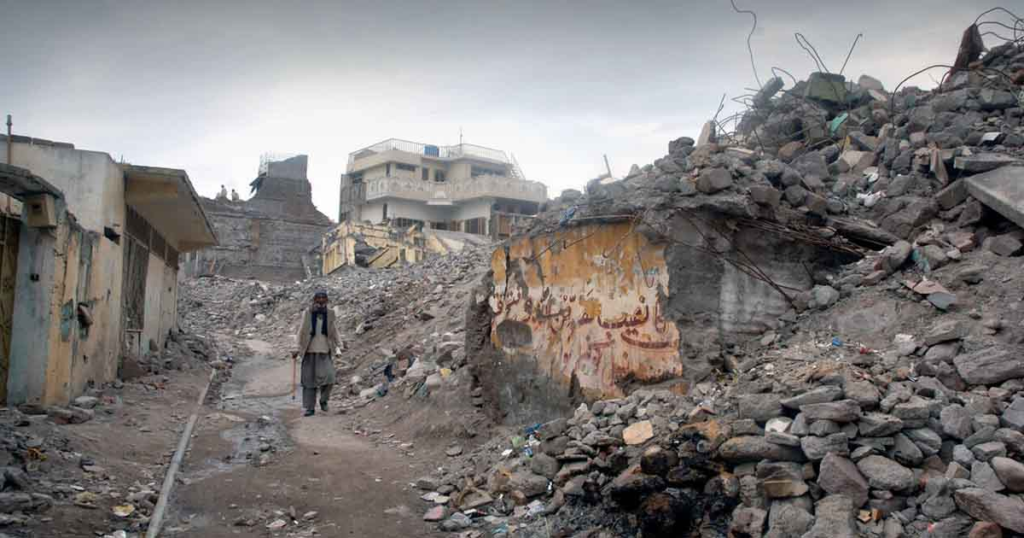

Aftershocks and Their Impact
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 was followed by a series of aftershocks, some of which were as strong as magnitude 6.2. These aftershocks caused further damage to already weakened structures and made rescue efforts more challenging. The earthquake also triggered landslides, which blocked roads and made it difficult to reach affected areas. The aftershocks and landslides compounded the damage caused by the initial earthquake, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters to have ever occurred in South Asia.
Destruction Unveiled
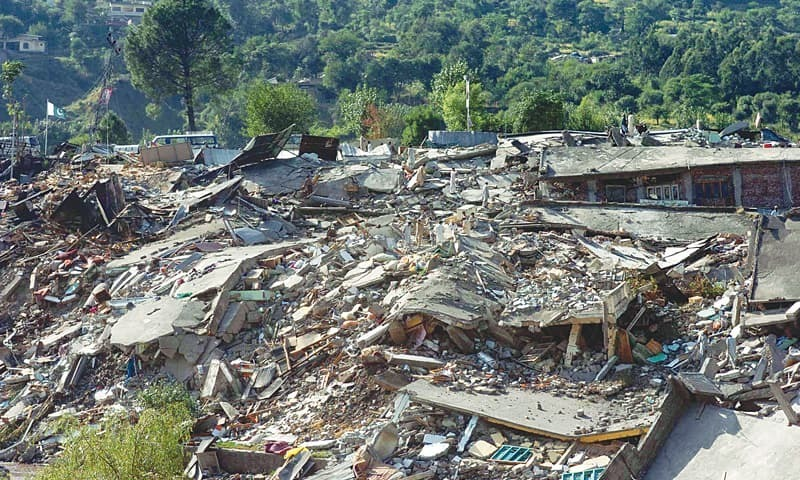

Immediate Aftermath and Damage Assessment
The immediate aftermath of the Kashmir earthquake of 2005 was characterized by widespread destruction and chaos. The earthquake caused massive damage to infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings. The destruction was so severe that it was difficult for rescue teams to reach affected areas.
Initial damage assessments revealed that over 32,000 buildings had collapsed in Kashmir alone, with many more damaged beyond repair. The earthquake also triggered landslides, which blocked roads and made it difficult to reach affected areas. The extent of the damage was so severe that it took years to rebuild the affected areas.
Casualties and Injuries
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 resulted in the loss of over 79,000 lives. The majority of these deaths occurred in Pakistan-administered Kashmir, where over 73,000 people lost their lives. The earthquake also left an estimated 4 million people homeless.
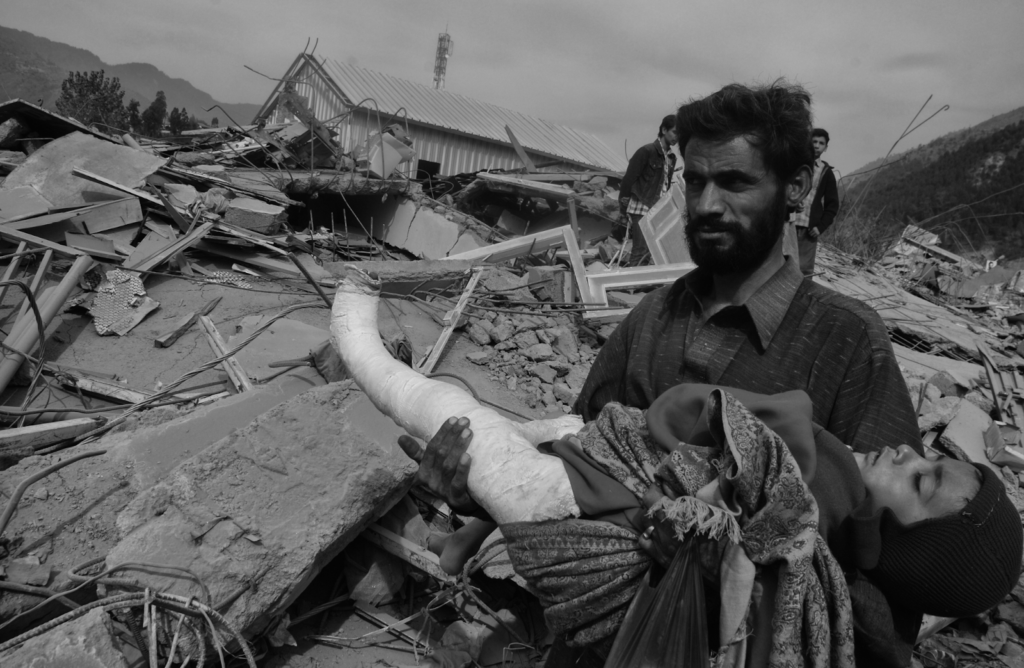

Major Destruction in Muzaffarabad and Surrounding Areas
Muzaffarabad, the capital city of Azad Jammu and Kashmir, was one of the worst-affected areas in the earthquake. The city suffered extensive damage to its infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings. Many significant landmarks and structures were also destroyed or damaged beyond repair.
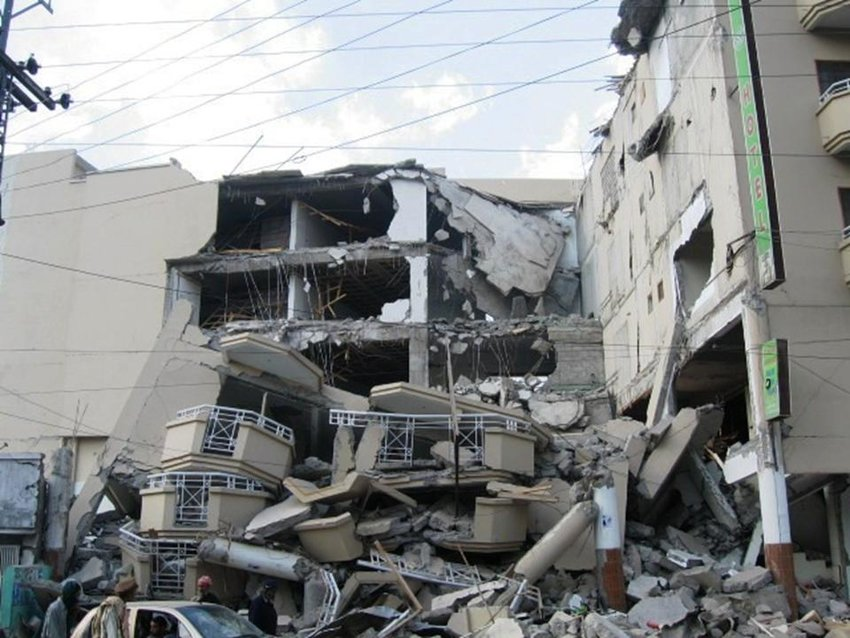

International Response and Relief Efforts
Immediate International Aid and Response
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 triggered an immediate international response, with many countries, international organizations, and non-governmental organizations offering relief aid to the affected regions. The aid given was in the form of monetary donations and pledges, as well as relief supplies, including food, medical supplies, and shelter. Some of the countries that contributed to the relief efforts include the United States, China, Japan, Australia, and the United Kingdom.
Role of NGOs: The $6.2 Billion Aid for Reconstruction
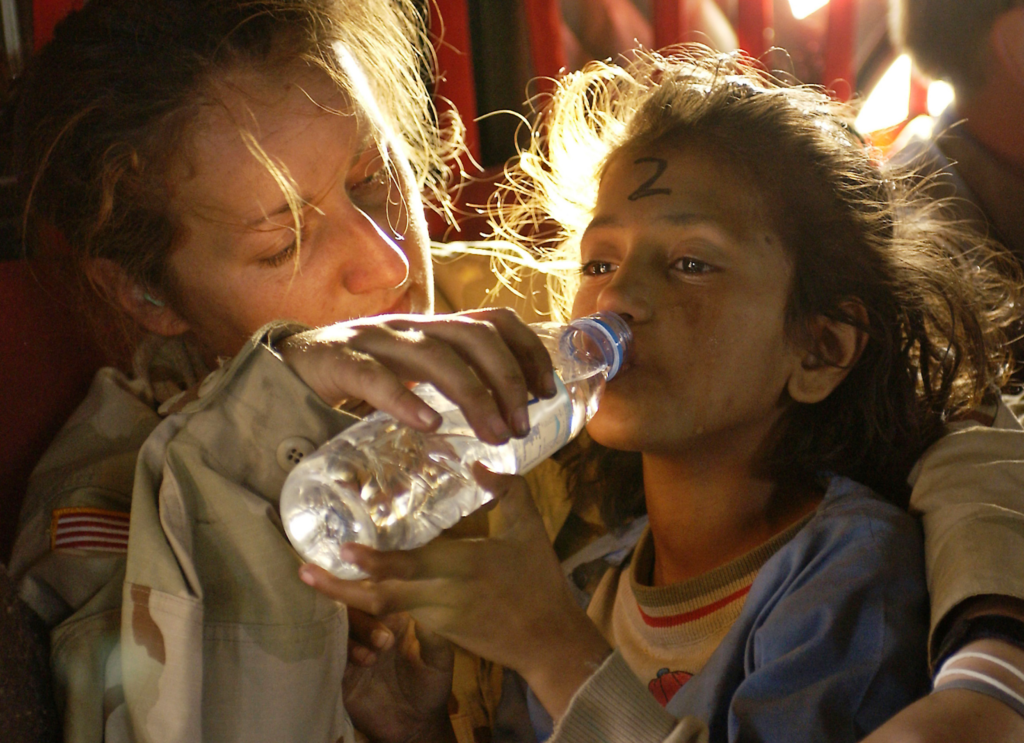

Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) played a significant role in the relief efforts following the Kashmir earthquake of 2005. NGOs used their expertise and experience in disaster response to ensure that relief efforts were efficient and effective and to reach the most vulnerable and marginalized communities. NGOs also played a crucial role in longer-term recovery efforts, working to rebuild homes, schools, and other infrastructure destroyed by the earthquake. The international support and solidarity witnessed during the 2005 Kashmir Earthquake were once again evident in the aftermath of the Turkey Syria Earthquake, emphasizing the importance of a united global response to natural disasters.
The international community pledged over $6.2 billion in aid for reconstruction efforts following the earthquake. This aid was used to rebuild homes, schools, hospitals, and other infrastructure destroyed by the earthquake. The funds were also used to provide support to those who had lost their homes or livelihoods due to the earthquake.
US Army and UK’s Royal Air Force Involvement
The US Army and the UK’s Royal Air Force played a significant role in the relief efforts following the Kashmir earthquake of 2005. The US Army sent a 180-strong civilian and military medical and emergency response team from state and territory health agencies and Australian Defence Force personnel. This task force treated more than 11,000 patients, working in a temporary health center in the central Punjab province. The UK’s Royal Air Force also provided support by airlifting supplies and personnel to affected areas.
Rebuilding and Recovery

Rehabilitation Efforts and Challenges Faced
The rehabilitation efforts following the Kashmir earthquake of 2005 were extensive and challenging. The government of Pakistan, along with international organizations and non-governmental organizations, worked together to provide relief aid to the affected regions. The aid was used to rebuild homes, schools, hospitals, and other infrastructure destroyed by the earthquake. The funds were also used to provide support to those who had lost their homes or livelihoods due to the earthquake.
However, the rehabilitation process was not without its challenges. The mountainous terrain of the affected regions made it difficult to reach some areas, and landslides blocked roads and made it difficult to transport relief supplies. The lack of infrastructure in some areas also made it challenging to provide aid to those in need.
Infrastructure Restoration and Development
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 had a significant impact on the infrastructure of the affected regions. Many buildings, roads, bridges, and other infrastructure were destroyed or damaged beyond repair. In response, the government of Pakistan launched several infrastructure restoration and development projects in the affected regions.
Some of the major infrastructure projects undertaken post-earthquake include the construction of new roads and bridges, the rebuilding of schools and hospitals, and the restoration of water supply systems. These projects aimed to improve access to basic services and promote economic growth in the affected regions.
Long-Term Impact on the Region and Its People
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 had a lasting impact on the region’s socio-economic landscape and its inhabitants. The earthquake caused widespread destruction and loss of life, leaving many people homeless or without access to basic services such as water, electricity, and healthcare. The event also highlighted the need for better disaster management and emergency response systems in the region.
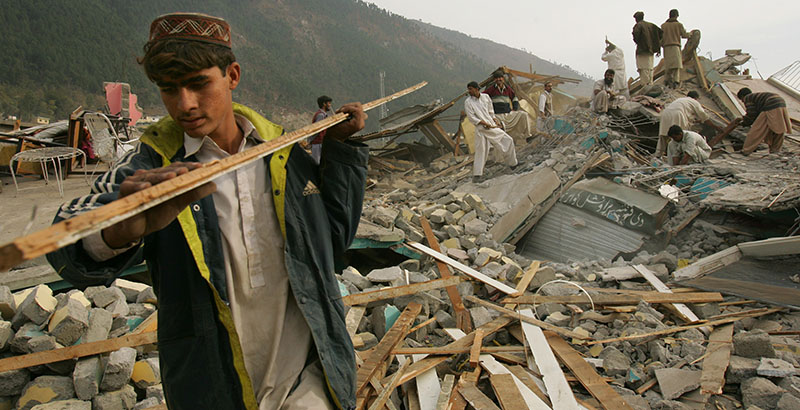

Lessons Learned
Importance of Preparedness for Natural Disasters
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 serves as a reminder of the importance of being prepared for natural disasters. The event highlighted the need for better disaster management and emergency response systems in the region. It also emphasized the importance of educating communities on disaster preparedness and response.
Measures such as creating early warning systems, developing evacuation plans, and conducting regular disaster drills can help minimize the impact of natural disasters. It is also essential to have adequate resources and trained personnel to respond to emergencies quickly and efficiently.
Measures Taken Post-Earthquake for Future Prevention
In response to the Kashmir earthquake of 2005, several policies, structures, and systems were put in place to prevent similar disasters from occurring in the future. The government of Pakistan established the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) to coordinate disaster management efforts across the country. The NDMA is responsible for developing policies and guidelines for disaster management, as well as coordinating relief efforts during emergencies.
The earthquake also led to the development of new building codes and standards aimed at making buildings more resistant to earthquakes. These codes require buildings to be constructed using earthquake-resistant materials and techniques, such as reinforced concrete frames and shear walls.
Verdict
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 was a catastrophic event that had far-reaching consequences for South Asia. The earthquake caused widespread destruction and loss of life, leaving many people homeless or without access to basic services such as water, electricity, and healthcare. However, the resilience and spirit of the affected communities were remarkable. The rehabilitation efforts following the earthquake were extensive and challenging, but they have helped rebuild homes, schools, hospitals, and other infrastructure destroyed by the earthquake.
The Global Unity in Response to the Disaster
The Kashmir earthquake of 2005 triggered an immediate international response, with many countries, international organizations, and non-governmental organizations offering relief aid to the affected regions. The global solidarity and unity shown in response to the disaster were heartening. The aid given was in the form of monetary donations and pledges, as well as relief supplies, including food, medical supplies, and shelter. The international community pledged over $6.2 billion in aid for reconstruction efforts following the earthquake.
In conclusion, while the Kashmir earthquake of 2005 was a devastating event that had far-reaching consequences for South Asia, it also highlighted the importance of disaster preparedness and emergency response planning. The event serves as a reminder of the need for better disaster management and emergency response systems in the region.



